Table of Contents
1. CAP
Cassandra一般被定义为AP系统(HBase是CP系统),因为只保证Eventual Consistancy。
根据这两篇文章,是否选择Cassandra的主要考虑因素是对Consistency的要求。Facebook的messaging system选择HBase而不是Cassandra,因为他们需要用户在发送Message后能马上知道是否发送成功。
Cassandra可以在通过客户端保证一致性。但是一个问题是,如果读写访问的是不同的节点,写后马上读可能会返回失败(虽然过一会可能就成功了)。
例如节点有ABCDE,W=3,R=3,W+R=6>5,因此能保证一致性。加入一个客户端X写入ABC后,另外一个客户端Y读取CDE,因为有延迟,Y的读取可能会返回失败(同步后读取会返回成功)。
On the contrary to the strong consistency used in most relational databases (ACID for Atomicity Consistency Isolation Durability) Cassandra is at the other end of the spectrum (BASE for Basically Available Soft-state Eventual consistency). Cassandra weak consistency comes in the form of eventual consistency which means the database eventually reaches a consistent state. As the data is replicated, the latest version of something is sitting on some node in the cluster, but older versions are still out there on other nodes, but eventually all nodes will see the latest version.
More specifically: R=read replica count W=write replica count N=replication factor Q=QUORUM (Q = N / 2 + 1)
|
2. 关键概念
- 类似于Mysql中的database,Cassandra中有keyspace的概念。
- 类似于mysql的table,每个keyspace有多个table
- 类似于mysql的row,每个table有多个row
- 每个row有一个primary key和多个column
- 每个primary key有一个partionion key和0-1个cluster key。
- 每个partition key可以有0-N个子key组成
- 每个cluster key可以有0-N个子key组成
- 每个casssandra cluster包含多个nodes
- 同一个table的不同row,根据partition key分布到各个node
如下面的table:
CREATE TABLE example (
partitionKey1 text,
partitionKey2 text,
clusterKey1 text,
clusterKey2 text,
normalField1 text,
normalField2 text,
PRIMARY KEY (
(partitionKey1, partitionKey2),
clusterKey1, clusterKey2
)
);- primary key为(partitionKey1, partitionKey2), clusterKey1, clusterKey2
- partition key为(partitionKey1, partitionKey2)
- cluster key为clusterKey1, clusterKey2
- column有: normalField1和normalField2两个
存储时,可以理解为: - 每个行的所有列挨在一起存储,以partition key作为索引 - 不同于mysql,每行的column在存储时除了记录column的value外,还需要编码column name - 编码的column name = cluster value + column name,因此同一个column,如果cluster key不同,编码后的column name不同
下面的数据
INSERT INTO example (
partitionKey1,
partitionKey2,
clusterKey1,
clusterKey2,
normalField1,
normalField2
) VALUES (
'partitionVal1',
'partitionVal2',
'clusterVal1',
'clusterVal2',
'normalVal1',
'normalVal2');
存储后类似于:
RowKey: partitionVal1:partitionVal2
=> (column=clusterVal1:clusterVal2:, value=, timestamp=1374630892473000)
=> (column=clusterVal1:clusterVal2:normalfield1, value=6e6f726d616c56616c31, timestamp=1374630892473000)
=> (column=clusterVal1:clusterVal2:normalfield2, value=6e6f726d616c56616c32, timestamp=1374630892473000)3. Cassandra数据建模
数据模型介绍如何合理的设计Table(Schema)。关于数据模型的介绍,以下资料比较清楚:
对Cassandra数据模型比较通俗易懂的解释来自于: teddyma - Learn Cassandra - Data Model & CQL
简而言之,Cassandra中的一个table可以看出一个 Map<RowKey, SortedMap<ColumnKey,ColumnValue>>。即每个table有很多row,并且以row key为索引。每个row有很多column。同一个row的数据挨着一起存放(下面详细介绍),不同column以 column key排序。
For each column family, don’t think of a relational table. Instead, think of a nested sorted map data structure. A nested sorted map is a more accurate analogy than a relational table, and will help you make the right decisions about your Cassandra data model.
``Map<RowKey, SortedMap<ColumnKey, ColumnValue>>`` 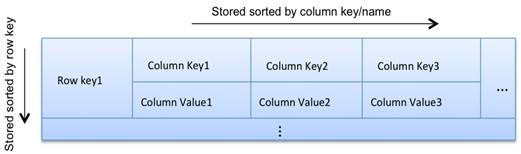 |
4. 存储引擎
Cassandra uses a storage structure similar to a Log-Structured Merge Tree, unlike a typical relational database that uses a B-Tree.
5. 数据的写入
Cassandra在写方面的主要消耗在写入和后期的维护,这个mysql不太一样(主要就是写入)。
下图是比较经典的关于Cassandra写路径的图:
写入分为三步:
- 写入commit log
- 写入memtable
- Flush memtable to (a new ) sstable ( sorted string table )
其中的memtable和sstable是各个表分开维护的。commit log用来保证断电等异常情况下,数据不丢失。memtable在内存中,用来提高读写速度,其中的的数据是排序的。当memtable大小超过临界值时,数据将flush到sstable。sstable中的同一个row的数据是挨在一起放的,row内的数据以clustering key的数据排序。flush memtable时,会创建新的sstable,而不会再更改该sstable。
我们说的插入、删除、修改,都是以column为单位的。
虽然在同一个sstable中,同一row的数据是挨着一起放的,但是同一row数据可以存在于多个sstable中。既同一个row的不同column可以存在于不同的sstable中。道理很简单,cassandra运行以column为读写单位,不同时间的读写如果涉及不同的column,不可能把不相关的column都在新的sstable中再写一遍。
数据的修改和删除也可以被当作写入来考虑。修改不会去现有的sstable中删除数据,而是会写入新的数据到新的sstable。删除就是写入一个特殊的标识。对于某row的某个column,Cassandra根据时间戳来合并各sstable的值。
6. 数据的维护及Compaction Strategy
Cassandra中数据维护的主要目的是提高后期的读效率。每次flush memtable都创建sstable。因为memtable一般不大,理论上就有N个sstable。因为同一个row的数据能存在于不同的sstable,那获取任意row就要查找所有的sstable。
当然,Cassandra有些加速机制。每个sstable维护了以下信息:
- Bloom filters, which can tell when a partition key is not in an SSTable.
- Minimum & maximum clustering keys, which can help rule out a number of SSTables.
- Minimum & maximum timestamps, which lets Cassandra reason about whether updates or deletes of values could have come after a particular value was written.
- (Hashed) partition key ranges, which in case Leveled Compaction Strategy is used, significantly reduces the number of potential SSTables to look in.
但这样还不够,于是Cassandra中就有一个Compaction的过程,用来整理sstable,提高read效率。需要注意的是,compaction过程也不会修改sstable,而只会新建和删除。
Cassandra目前有三种Compactin策略,需要根据实际应用去选择,也就是理论上不同的table需要选择不同的策略。他们是:
- Size-Tied Compaction Strategy (STCS)
- Leveled Compaction Strategy (LCS)
- Date-Tied Compaction Strategy (DTCS)
6.1. STCS
STCS就是把类似大小的sstable合并在一起。
6.2. LCS
LCS需要注意的是:
- 不同的Level的单个sstable的size是一样的,不同的level只是sstable个数不同。
- 同level中的sstable之间row key是不会overlap的,而且L+1的sstable个数是L的10倍,因此能保证90%的读只需要访问一个sstable,而最差情况是需要访问ML个sstable(ML是max level)
- 对于以write为主的table,LCS非常不合适,因为每个level都有大小限制,当低的满时,需要往高的level merge,这很可能需要重新生成高level的所有sstable。
6.3. DTCS
DTCS顾名思义适用于Date Series数据,但是它有两个前提:
- writes come at a somewhat steady rate,
- timestamps roughly reflect the time of arrival to Cassandra
Compaction的过程可以用DataStax提供这张图解释:

我们先确定一个有多个windows组成的滑动窗口序列(图中的几道竖线)。
- 序列的第一个(离now最近的)窗口的大小由变量base_time_seconds 决定
- 第N+1个windows窗口大小是第N个的min_threshold倍。
随着时间的推移,我们把这个滑动窗口序列往前推移。推移过程中,最老时间戳属于同一个window的sstable数量如果大于min_threshold个,则合并。
